The next generation of AI has arrived. Here’s how it works – and why it will be revolutionary for business and society
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it is a reality, reshaping industries and redefining how businesses operate. And the technology is advancing at break-neck pace. We saw organizations start using prediction-based machine-learning algorithms around 2017, before moving to generative AI (GenAI), exemplified by models like ChatGPT, in 2023. We are now at the cusp of another big step up: agentic AI.
The arrival of agentic AI is likely to represent a paradigm shift. It goes beyond the reactive capabilities of traditional AI to create systems capable of autonomous decision-making and proactive action. Such unprecedented capabilities will undoubtedly alter the future business landscape.
What is agentic AI?
Traditional AI systems operate on fixed rules and require explicit instructions for every task. GenAI excels at producing content, text, images and other media in response to specific user prompts. But agentic AI represents a significant leap forward, as it can execute tasks and make decisions independently toward defined objectives.
Let’s use an analogy. Traditional AI is like a recipe book, providing instructions for dish preparation. On the other hand, GenAI is akin to a recipe generator, offering a new dish following the inputted requirements. In contrast, agentic AI functions like a personal chef, managing the entire meal preparation process from menu planning to serving the final dish. Three fundamental attributes characterize AI agents.
Autonomy
AI agents can execute complex tasks without constant human supervision. When given a high-level objective, such as optimizing a supply chain or managing customer relationships, the AI can independently find, determine and implement the necessary steps to accomplish the stated goals.
Adaptability
These systems learn by doing, and adapt their performance through outcome analysis and data integration. In customer service applications, for example, agentic AI can evolve to take on increasingly sophisticated operations over time.
Goal orientation
Agentic AI is designed to achieve specific business goals. Hence, unlike previous AI algorithms, AI agents are proactive. For instance, when asked to plan a vacation, AI agents can analyze conditions and requirements, identify local events and festivals during that time, and develop and propose (or even implement) solutions.
It is precisely due to these attributes that agentic AI is seen as a ‘do it yourself’ approach that will supercharge the next generation of the ‘do-it-for-me’ economy. It could substantially change how users access services and market structures. The internet era reshaped the economy and society. AI – and especially agentic AI – will likely lead to even greater change.
How agentic AI operates
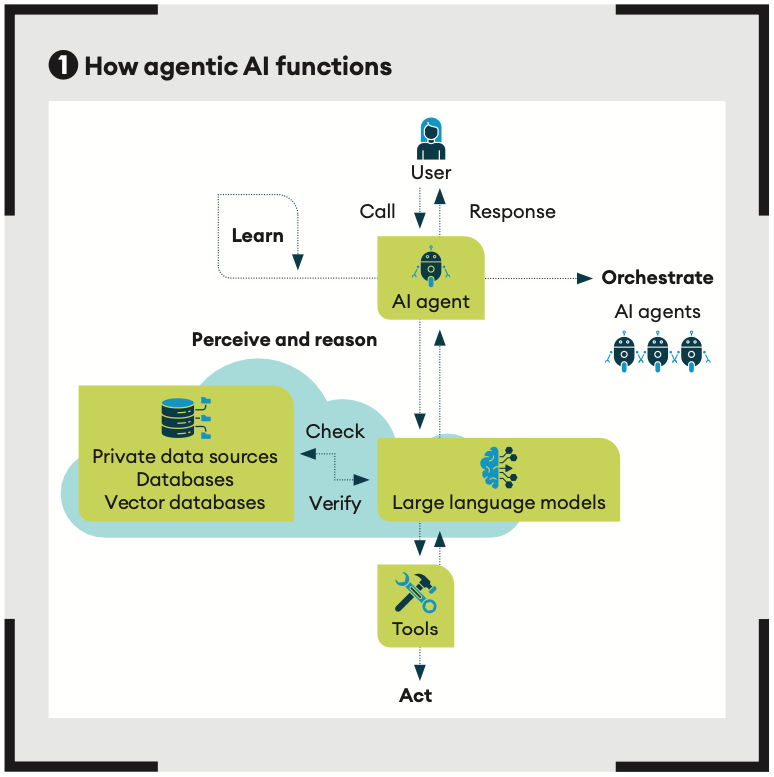
To understand exactly how agentic AI functions, let’s break down the five steps it takes (as illustrated in Figure 1).
1. Perceiving
An agent gathers and processes data from various information sources
2. Reasoning
It uses GenAI to understand tasks, generate solutions and coordinate specialized AI models for specific functions, such as content creation and recommendation systems
3. Acting
The agent executes tasks using various tools, such as spreadsheets or customized user interfaces, based on the goal to be reached. What makes agentic AI so powerful is the combination of these two steps, reasoning and acting: they enable an agent to ‘ReAct’
4. Learning
The agent improves its performance through feedback and experience, becoming more effective and efficient in making decisions over time
5. Orchestrating
An agent shares information and collaborates with other AI agents to solve increasingly complex problems, delivering better user performance.
To put it another way, an AI agent functions like a highly skilled personal assistant who understands objectives and proactively works towards achieving them without constant direction.
A transformative impact
Today’s AI agents can only handle specific undertakings, but they are set to be able to take on multiple tasks simultaneously. As this technology continues to develop, it is not hard to imagine that agents will be able to replace many of today’s jobs. Such an impact will be felt both within and outside of companies. Businesses using agentic AI are likely to make fewer hires and have fewer organizational layers. Business functions themselves will also change, including IT: “The IT department of every company is going to be the HR department of AI agents in the future,” as Nvidia’s boss Jensen Huang has said.
Extending this logic, we could see many company departments shrink to become a ‘department of one.’ A single human could give directions that are implemented by a workforce of AI agents. Creating a ‘unicorn of one’ – a tremendously successful startup where the founder is the only staff member – is not impossible.
But in the near term, agentic AI is poised to revolutionize various industries, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation. Healthcare is one. Agentic AI can analyze medical data, assist in diagnostics and provide continuous patient monitoring. Such systems support medical professionals by offering real-time data during procedures and suggesting treatment plans, ultimately improving the quality of care delivery.
Finance is another. Agentic AI techniques are already being used (including by Nexus FrontierTech) to help lending teams at global banks collect and analyze environmental and sustainability data. This enables them to efficiently approve new loans and monitor existing ones in real time. AI agents can also help improve compliance and regulatory analysis, such as evaluating transactions flagged for sanctions.
Supply chain businesses are also likely to see major changes. Agentic AI can optimize inventory, predict disruptions and reconfigure supply chains in real time. By autonomously managing inventory and planning delivery routes, AI-based delivery systems can reduce fuel consumption and increase global logistics efficiency.
Within organizations, AI agents will also raise workflow efficiency. Customer service is likely to be a primary area for deployment. AI agents can automate routine interactions, answer queries and resolve issues with speed and accuracy. They can also offer personalized responses and even predict potential problems before they arise. A recent industry report by UiPath pointed out that 51% of surveyed IT executives believe that increased customer responsiveness will be a benefit of adopting agentic AI.
Document processing will also benefit. Agentic workflows can significantly streamline workflows for extracting and processing information from financial complex documents. This approach enhances accuracy, reduces the need for extensive programming, and allows for adaptation to various document types and information requirements.
All in all, agentic AI has the potential to rewrite many of today’s business rules. Cloud computing and the internet changed the economics of business, shifting the focus from capital expenditure to operating expenditure, and thereby giving rise to the software-as-a-service business model. Similarly, agentic AI is causing fundamental changes that will surely lead to brand new business models and ways of operation. Companies embracing agentic AI will probably be better positioned to adapt to the evolving digital landscape and gain a competitive edge.
The downsides of agentic AI
While agentic AI offers numerous benefits, it also presents significant challenges and considerations that businesses must address to ensure responsible and sustainable adoption.
One of the most significant long-term consequences lies in how agentic AI will transform the nature of work. On the one hand, as AI agents automate routine tasks, human workers can focus on higher-value activities that require critical thinking, creativity and emotional intelligence, leading to more fulfilling work and higher job satisfaction. Indeed, the shift to agentic AI will create new opportunities, roles and jobs. However, in the longer run, agentic AI will move business economics away from employee payroll and toward software subscription. Companies will be spending more on IT but offering fewer jobs.
The future of employment can be expected to be highly unpredictable. The primary challenge will not be an absence of jobs, but rather the need for continuous retraining and adaptation to a constantly evolving job market. Financial struggles will likely arise, particularly for individuals who have lost their jobs while they transition and acquire new skills. Psychological difficulties will also emerge in these individuals. These will raise significant challenges for employers and society as a whole.
There is also the question of accountability if human users are delegating decision-making to AI. If an AI agent makes a mistake, who is responsible? The AI? The company itself? Or the technology provider? And how do businesses buy insurance against the financial consequences of such mistakes? Indeed, what measures must be put in place to ensure that AI systems do not perpetuate biases in their decision making?
Like all machines, AI agents can malfunction, leading to operational breakdowns. AI agents may exploit loopholes in their programming to achieve objectives through unintended shortcuts, rather than fulfilling their intended goals. Agents might inappropriately apply learned goals to unforeseen situations, or appear aligned with intended objectives during training while in fact harboring different internal goals.
There is also the potential for agentic AI to be used maliciously. Just as GenAI is now being used to write sophisticated and personalized fraud emails, AI agents can be abused to facilitate more elaborate scams by creating more convincing and personalized content at unprecedented speeds. Guardrails and guidelines will be essential to ensure agentic AI’s responsible and ethical deployment. New legal and compliance frameworks will be necessary to explicitly address the issue of accountability for AI agents.
Organizations must implement rigorous security audits to protect data and ensure regulatory compliance as these systems become more integrated with enterprise applications and infrastructure. Establishing a secure foundation for AI-driven initiatives is essential to safeguarding operations, reputation and customer trust, and is also necessary to fend off cyberattacks.
The coming agentic AI era
Agentic AI signifies a groundbreaking advancement in technology. It transcends the mere execution of instructed tasks to engage instead in autonomous, proactive problem-solving. As these systems evolve and become more sophisticated, they will be able to address increasingly intricate challenges, fostering unprecedented efficiency and creativity across various industry domains.
Agentic AI could create new economic activities, with startups large or small; highly specialized AI agents will likely be produced and made available on the market. Indeed, there are signs that technology vendors will offer small language models that could be better suited for working with AI agents, as they demand much less computing resources.
For companies, embracing agentic AI will likely confer strategic advantages, enabling them to adapt more swiftly to the rapidly changing digital landscape. In an era where automation is becoming increasingly prevalent, organizations that integrate agentic AI into their operations will gain unprecedented operational efficiency, thereby optimizing processes and workflows.
However, successfully adopting agentic AI requires a thoughtful and balanced approach. It is crucial to maximize the benefits these systems offer, while simultaneously addressing the societal, security and ethical challenges they present. This involves investing in comprehensive training programs to upskill employees, developing robust and secure infrastructure to support AI integration, and implementing stringent governance frameworks to ensure responsible deployment.
By navigating these complexities with foresight and responsibility, businesses can harness the full potential of agentic AI, paving the way for a future where human ingenuity and artificial intelligence work in seamless harmony.




